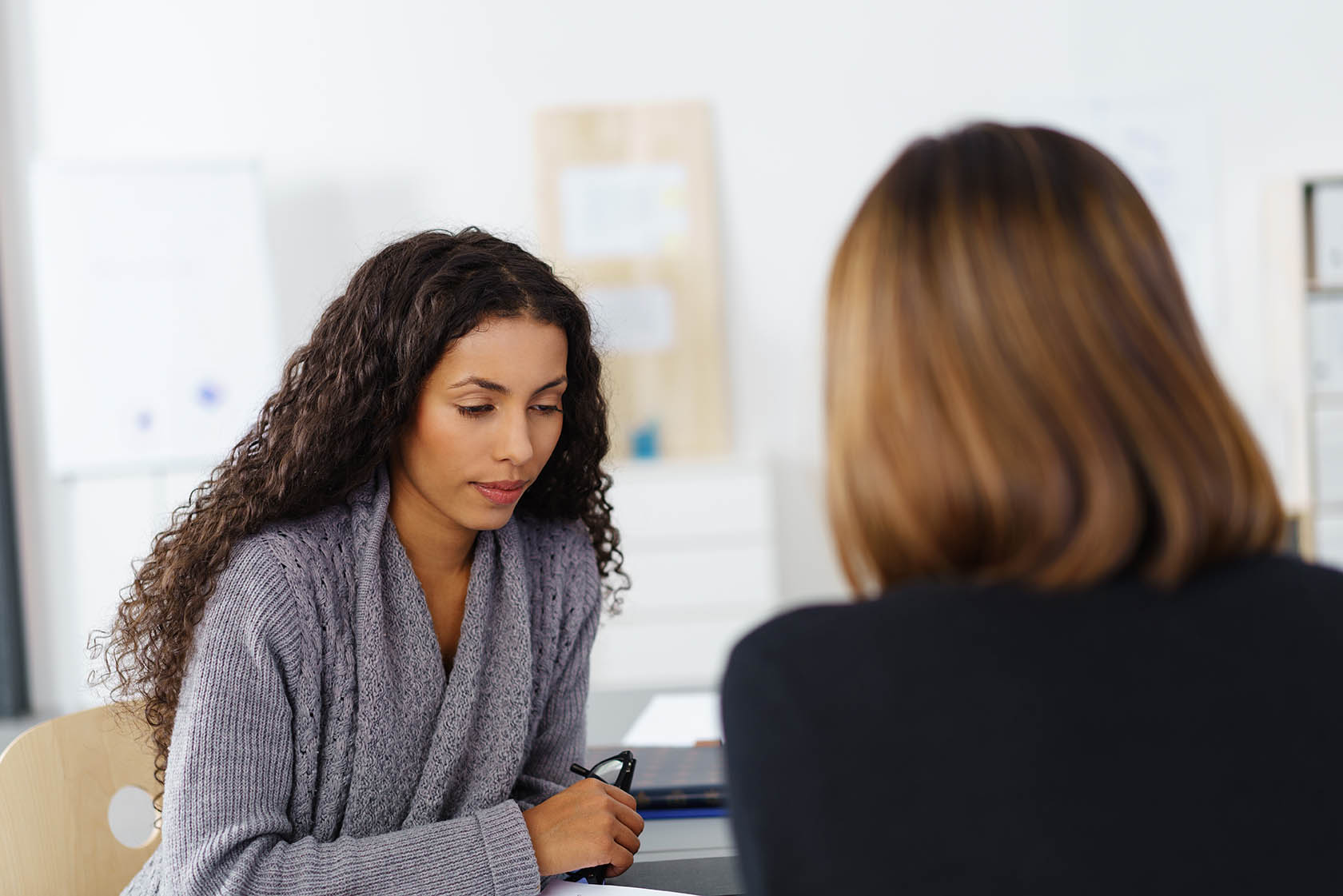

Workplace complaints may start as whispers or emails, yet your response shapes trust and culture; a calm, structured approach protects relationships and preserves morale and reputation.
Why begin with a clear definition?
What counts as a complaint in your setting? A complaint is any expression of dissatisfaction. It may arrive verbally, in writing, or through a representative. It can concern behavior, process, pay, or safety. Definitions protect both managers and employees from confusion. According to our editor’s research, clarity reduces cycle time dramatically. A simple definition also guides routing and documentation.
What early triage prevents bigger problems?
Begin with a short intake and respectful acknowledgment. Confirm basic facts and desired outcomes clearly. Decide whether the issue is informal or formal. Explain the next steps and timeframes carefully. Keep the door open for informal resolution. People want to know when they will hear back. ACAS guidance stresses fair, transparent procedures for grievances. These principles anchor trust and tribunal resilience.
How should you receive a complaint professionally?
Show calm body language and steady tone. Listen without interrupting or judging. Reflect back the core concern concisely. Ask neutral questions that open detail. Avoid leading or accusatory phrasing entirely. Offer privacy and a quiet setting immediately. According to our editor’s research, early empathy reduces escalation. The goal is clarity, not speed or closure.
What should you document and when?
Document dates, times, people, and claims. Capture exact words where possible. Separate fact, observation, and interpretation. Store documents in a secure location. Limit access to need to know roles. Keep versions controlled and traceable. Note every contact with the complainant. As a result of our editor’s reviews, contemporaneous notes carry weight. Good records support fair decisions and appeals.
How do you assess risk and route cases?
Screen for safety, retaliation, discrimination, and legal exposure. Safety concerns bypass normal timelines. Retaliation risks require protective steps quickly. Discrimination claims demand strict objectivity and pace. In the United States, OSHA protects whistleblowers. Escalate those matters to specialist teams. In the UAE, MoHRE handles labor complaints. Direct people to official channels when appropriate. Internal handling continues in parallel where possible.
What makes an investigation fair and focused?
Appoint an impartial investigator with capacity. Agree a written scope and questions. Gather documents before interviews whenever possible. Interview parties in a consistent sequence. Use open prompts and specific follow ups. Offer a support person where policies allow. Test facts against corroborating evidence. ACAS materials emphasize procedural fairness across steps. That approach reduces challenge later.
How should you communicate while investigating?
Set expectations for updates at intake. Offer a named contact for questions. Acknowledge delays before people ask. Avoid promising specific outcomes prematurely. Explain how decisions will be reached. Share a simple timeline with key stages. Thank participants for cooperation and patience. According to our editor’s research, cadence prevents rumor. Trust grows when silence is avoided.
Which standards can guide your complaint system?
ISO 10002 outlines complaint handling principles. It promotes consistency, learning, and customer focus. Its language translates well to internal settings. Map your workflow to its key clauses. Use it to frame metrics and reviews. Standards accelerate training and cross team alignment. They also support audits and improvements. As a result of our editor’s reviews, alignment speeds adoption. The structure helps leaders allocate effort wisely.
How do you treat harassment and violence reports?
Adopt a zero tolerance stance in policy. Prioritize safety and stop ongoing harm fast. Provide confidential channels with clear protections. Consider interim measures that limit contact. Keep evidence secure and interviews respectful. ILO Convention 190 frames international expectations. It recognizes a right to a safe workplace. Local law then sets specific duties and remedies. Use both lenses for decisions.
What outcomes feel proportionate and fair?
Base outcomes on evidence and policy language. Consider intent, impact, and prior conduct. Offer coaching or training for low risk cases. Use mediation only when appropriate. Apply discipline where rules require it. Explain the rationale in plain language. Outline appeal routes without defensiveness. According to our editor’s research, transparency reduces repeat conflict. People accept decisions they can understand.
How do you convert complaints into improvements?
Track themes and recurring failure points. Look for process friction that breeds frustration. Fix small pain points that compound stress. Close policy gaps that allow confusion. Improve signage, forms, and handoffs thoughtfully. Share quick wins with teams to build momentum. Invite frontline ideas for low cost changes. As a result of our editor’s reviews, small repairs matter. They often prevent bigger grievances later.
Which metrics are worth watching closely?
Measure time to first acknowledgment. Monitor time to resolution by category. Track satisfaction with the handling process. Record reopens within ninety days. Watch conversion from informal to formal cases. ISO 10002 encourages monitoring complaint data. Frequency and type reveal systemic issues. Share trends with leaders quarterly. Use data to tune staffing and training.
How can managers prepare for tough conversations?
Offer scripts for opening and closing. Train on empathy and neutrality. Practice handling anger calmly and safely. Use short summaries to confirm understanding. Avoid long debates in first meetings. Provide de escalation options for high stress moments. Encourage managers to book recovery time. According to our editor’s research, practice builds confidence. Confidence then improves fairness and pace.
How should you adapt for remote and hybrid work?
Create secure digital intake channels. Avoid personal messaging apps for official steps. Use identity verification for complainants. Offer video options for sensitive interviews. Protect locations and screen privacy carefully. Schedule shorter, more frequent sessions online. Provide digital evidence guidance for participants. Document time zones and local laws clearly. Hybrid design needs considered safeguards and etiquette.
What protects people who speak up?
Anti retaliation rules must be explicit. Train leaders on protected activities and rights. Set consequences for retaliatory behavior. Offer confidential reporting for bystanders. Explain how you monitor for subtle retaliation. OSHA materials describe whistleblower protections. Similar principles exist in many jurisdictions. Align your policy with local law. Reinforce protections at every stage.
How should you close cases and follow up?
Provide a written outcome letter promptly. Separate findings from recommendations clearly. Offer appeal options where policies allow. Confirm any agreed actions and timelines. Thank participants for their cooperation. Ask for feedback on the handling experience. Log lessons for future improvements. According to our editor’s research, closure reduces anxiety. Follow up proves the system truly works.
Which roles keep the system healthy?
Leaders set tone and model behavior. HR designs fair processes and training. Legal confirms compliance and risk posture. Security supports safety and evidence protection. Communications supports updates and templates. Facilities supports private rooms and access. Technology maintains secure case systems. Everyone owns culture and respect. The machine only runs when roles align.
What do employees need to feel safe?
Clear routes for informal and formal issues. Simple forms and nontechnical language. Confidentiality, within legal limits, explained plainly. Predictable timelines with named contacts. Respectful treatment in every interaction. Option to bring a colleague or representative. Feedback channels after resolution. As a result of our editor’s reviews, predictability drives trust. Trust encourages early, solvable complaints.
How do you tailor for local context?
Use national guidance where available. In the UAE, MoHRE offers complaint pathways. Reference these routes in your handbook. In the UK, ACAS provides grievance codes. In many countries, ILO principles guide dignity. Align internal policy with local frameworks. Teach managers jurisdictional differences simply. Keep a contact list for quick referrals. Local fluency prevents procedural mistakes.
What simple playbook can every team adopt?
Acknowledge quickly and respectfully. Triage risk and pick a path. Investigate impartially with defined scope. Communicate regularly and clearly. Decide fairly and explain reasons. Protect people from retaliation. Capture lessons and fix root causes. Train managers and practice scripts. Measure outcomes and publish trends. Repeat these habits until they feel natural.

 then "Add to Home Screen"
then "Add to Home Screen"